CHINASE | ENGLISH
bottom
NEWS
In-orbit Delivery of World First Land and Meteorological Hyper-spectral Observation Satellite Completed
On March 21, the in-orbit delivery of GF5 satellite, which was developed by Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, was successfully completed. As the world first land and meteorological hyper-spectral observation satellite, GF5 satellite can be used for observing the atmosphere, land surface, and mines. It has four strengths, namely, fine spatial resolution, hyper-spectral resolution, high time resolution, and high calibration accuracy. It can also provide quantitative high accuracy remote sensing data in the field of atmosphere, water, and ecological environment monitoring, and studies of global climatic change. It has been a powerful tool for strengthening China’s environmental pollution prevention, and can secure a greater say and promote influence of China in the world environment improvement system.

In the presence of Zhang Kejian, Vice Minister of Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and Director General of State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense, Wu Yanhua, Deputy Director General of State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defence, Lui Hua, Vice Minister of Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Ma Youxiang, General Livestock Engineer of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shang Yong, Vice Minister of Ministry of Emergency Management, Yu Xinwen, Deputy Director General of China Meteorological Administration, Peng Youdong, Deputy Director General of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Yuan Jie, General Manager of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, Shang Zhi, Director of the Department of Space Navigation of the Corporation and Dai Shoulun, President of Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology signed GF5 satellite in-orbit operation certificate and long-time operation management agreement with the user.

Ceremony of GF5 and GF6’s delivery for use
It is reported that GF5 satellite was successfully launched in China’s Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center on May 9, 2018. Nine-month strict in-orbit test & evaluation shows the functional and performance indicators are all satisfactory, and the payload data quality and inversion results are also excellent.
Images of GF5 whole spectral imager
|
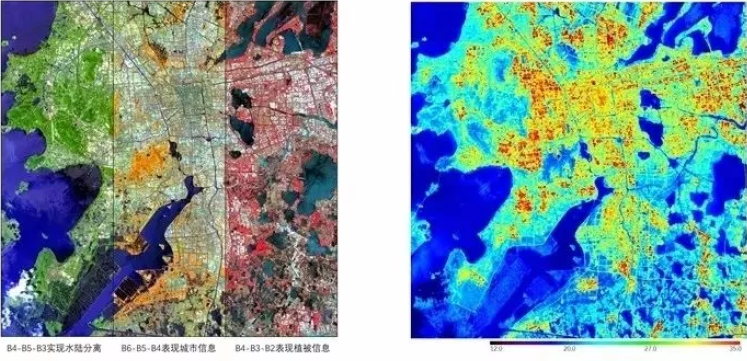
Pseudo-color composite image of Suzhou |
Urban heat island of Suzhou |
|||
|
|
||||
|
B4-B5-B3 realize separation of land and water data |
B6-B5-B4 display the city information |
B4-B3-B2 display the vegetation information |
|
|
|
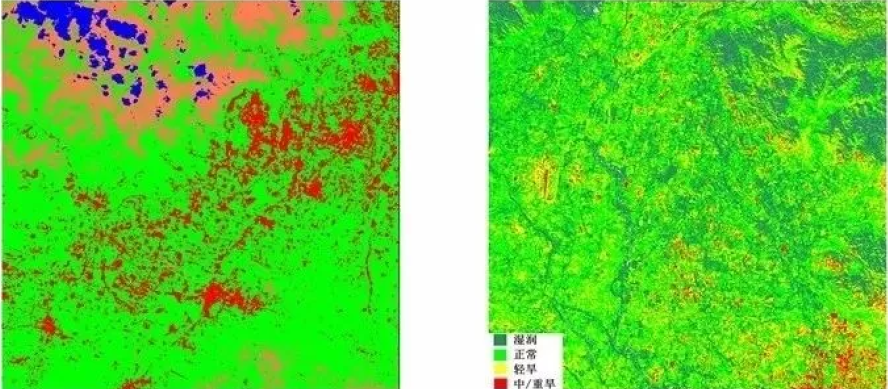
Distribution map of brightness temperature grade in southwest Beijing |
Drought monitoring image in southeast Beijing |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
Humid Normal Slight drought Medium/serious drought |
|||
|
The above left figure, with 20m spatial resolution obtained by the load, is a 60km wide pseudo-color composite map of different spectral coverage of Suzhou. Different ground targets can be monitored through fusion of different spectral coverage.The pseudo-color composite map of 810nm, 1650nm and 650nm spectral coverage can distinguish land and waters (the orange and green parts are land, blue parts are waters). Pseudo-color composite map of 2215nm, 1650nm and 810nm spectral coverage is city monitoring. Pseudo-color composite map of 810nm, 650nm and 560nm spectral coverage is vegetation monitoring (the red parts represent vegetation; the brighter the color is, the healthier the vegetation is). The above right figure is the monitoring map of urban heat island effect in the daytime in Suzhou obtained by the load. The figure shows the distribution of urban heat island effect in different areas. The left figure below is the distribution map of brightness temperature grade in southwest Beijing obtained by the load with 40m spatial resolution. In the map, red parts represent the high temperature targets, showing that the load can effectively monitor the high temperature in local areas. The right figure below is the distribution map of drought in southwest Beijing obtained by the load. The load can also obtain the visible-thermal infrared image at the same time, and can effectively monitor the degree of drought on the land surface through the visible-thermal infrared image. |
||||
|
Sensor. whole spectral imager Receiving time: June 1, August 5, August 26, 2018 |
Center for Important Projects, State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense Made by Satellite Environment Application Center, Ministry of Ecology and Environment National Satellite Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration China Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application
|
|||
As a space-based hyper-spectral observation satellite, GF5 can comprehensively improve China’s capability for pollution monitoring in the world, obtain large-scale environmental monitoring data fast, and effectively fill up the gap of China in precise monitoring of environmental pollution. It is also one of the most efficient methods and technologies for monitoring global climatic change, and is of great importance for China’s ecological development, environmental diplomacy and global environment treatment.
In the field of air pollution, GF5 satellite can precisely perceive the distribution, change and transfer process of major atmospheric pollutants like smog, O3, NO2 and SO2, and find out all gaseous pollutants precisely.
In the field of greenhouse gas, GF5 satellite can acutely perceive the whereabouts of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, trace their origin and predict their travelling, provide effective support to the studies of hot issues like global warming, and provide suggestions to energy conservation and emission reduction and environmental diplomacy decision making.
Data of major greenhouse gas monitor of GF5 satellite
Greenhouse gas CO2 inversion result of GF5 satellite
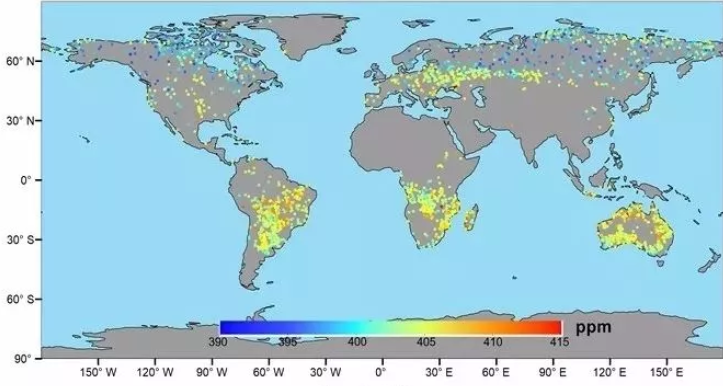
August 2018
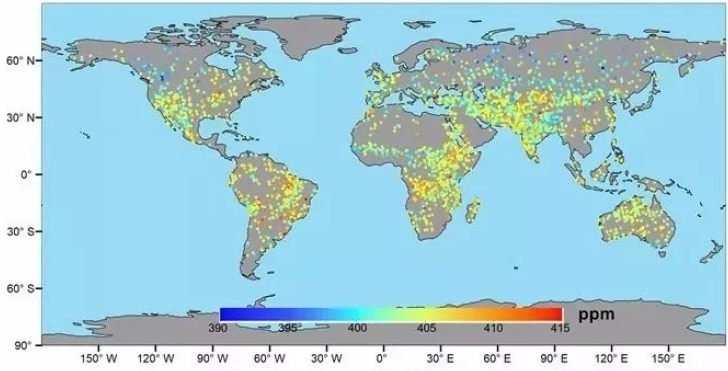
September 2018
|
The above figure is the global CO2 monitoring result in August 2018; the figure below is the global CO2 monitoring result in September 2018. They can clearly reflect the spatial distribution characteristics and fluctuation tend. In these two months, the CO2 concentration in the southern hemisphere is higher than that in the northern hemisphere, and the overall distribution trend is consistent with the monitoring result of a similar foreign satellite GOSAT, OCO-2. |
|
|
Sensor: Major greenhouse gas monitor Receiving time: August-September, 2018 |
Center for Important Projects, State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense Made by Satellite Environment Application Center, Ministry of Ecology and Environment National Satellite Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration
|
In the field of water pollution, GF5 satellite can precisely identify the water quality of potable water sources and key lakes and reservoirs, timely track the growth and change of alga pollutants in inland waters, such as blue algae, green algae and yellow algae, and provide solutions for water protection and pollution control.
Besides, GF5 satellite can also identify subsurface mines through surface imaging analysis. Like an eye of perspective, it can also play an important role in mineral resource investigation, geologic environment investigation and monitoring.
According to China’s spatial infrastructure plan, before 2022, China will launch one hyper-spectral observation satellite, one atmosphere monitoring satellite and one high accuracy comprehensive greenhouse gas monitoring satellite to constitute the space-based comprehensive environment monitoring system. Development of these satellites will be taken charge of by Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. Through networking of several satellites and team working of several loads, the monitoring efficiency and monitoring capability of this system can be greatly multiplied. Besides, with addition of the active detection means, it can combine active observation with passive observation to further improve the monitoring freedom and data accuracy, provide users high grade data with higher time efficiency, higher accuracy and wider coverage, and play a more important role in environment improvement, land resource survey, climate change study, disaster prevention and reduction, and agricultural and forestry monitoring.
Some pictures are taken from the official WeChat of Equipment Science and Technology and China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation.











 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD E-MAIL
E-MAIL